 Antibodi Immunosorbent Enzyme-linked (ELISAs) adalah teknik yang menggabungkan spesifisitas antibodi dengan sensitivitas uji enzim secara sederhana, dengan menggunakan antibodi atau antigen yang digabungkan ke suatu enzim yang mudah diuji. ELISA memberikan pengukuran antigen atau antibodi yang baik secara relatif maupun kuantitatif. ELISA dapat digunakan untuk mendeteksi adanya antigen yang dikenali oleh antibodi atau dapat digunakan untuk menguji antibodi yang mengenali antigen.
Antibodi Immunosorbent Enzyme-linked (ELISAs) adalah teknik yang menggabungkan spesifisitas antibodi dengan sensitivitas uji enzim secara sederhana, dengan menggunakan antibodi atau antigen yang digabungkan ke suatu enzim yang mudah diuji. ELISA memberikan pengukuran antigen atau antibodi yang baik secara relatif maupun kuantitatif. ELISA dapat digunakan untuk mendeteksi adanya antigen yang dikenali oleh antibodi atau dapat digunakan untuk menguji antibodi yang mengenali antigen.
Teknik ELISA seacara umum mengikuti lima prosedur 1) melapisi pelat microtiter dengan antigen;
2) memblokir semua situs yang tidak terikat untuk mencegah hasil positif palsu;
3) menambahkan antibodi primer (misalnya antibodi rabbit monoklonal ) ke sumur;
4) tambahkan antibodi sekunder yang terkonjugasi ke enzim (misalnya IgG anti-rat);
5) reaksi substrat dengan enzim untuk menghasilkan produk berwarna, sehingga menunjukkan reaksi positif.
Berikut adalah prinsip umum ELISA yang bisa dilakukan :
Indirect ELISA Protocol
| 1. Dilute antigen to a final concentration of 1-20 μg/ml using PBS or Bicarbonate/carbonate coating buffer. Coat the wells of a PVC microtiter plate with the antigen by pipeting 50μl of the antigen dilution in the top wells of the plate. Dilute down the plate as required. Seal the plate and incubate overnight at 4°C or 2 h at room temperature. 2. Wash plate 3 times with PBS. 3. Block the remaining protein-binding sites in the coated wells by adding 200 μl blocking buffer, 5% non fat dry milk/PBS, per well. Alternative blocking reagents include BlockACE or BSA. 4. Cover the plate with an adhesive plastic and incubate for at least 2 h at room temperature or, if more convenient, overnight at 4°C. 5. Wash the plate 3 times with PBS. 6. Add 100 μl of diluted primary antibody to each well. 7. Cover the plate with an adhesive plastic and incubate for 2 h at room temperature. 8. Wash the plate 4 times with PBS. 9. Add 100 μl of conjugated secondary antibody, diluted at the optimal concentration (according to the manufacturer) in blocking buffer immediately before use. 10. Cover the plate with an adhesive plastic and incubate for 1-2 h at room temperature. 11. Wash the plate 5 times with PBS. 12. Dispense 100 μl (or 50 μl) of the substrate solution per well with a multichannel pipet or a multipipet. 13. After sufficient color development (if it is necessary) add 50-100μl of stop solution to the wells. 14. Record the absorbance at 450 nm on a plate reader within 30 minutes of stopping the reaction. |
Direct ELISA Protocol
| 1. Coat ELISA plate (96 well plate) with testing antigen (10 μg/ml to 0.01 ng/ml in 50 mM Na2C03, pH 9.6, adjust based on the reactivity of antibody, 100 μl/well. Seal the plate and incubate overnight at 4°C. 2. Wash plate 3 times with PBS-T (0.05 % Tween-20 in PBS). 3. Block plate with 0.2% non-fat dry milk in PBS at room temperature for 1 hour at 4°C Note: Milk should be thoroughly dissolved. It’s recommended to dissolve 0.5 g milk in 50 ml PBS (1%) for at least 30 minutes at room temperature with rotation or stirring, then dilute to 0.2 %, and keep rotating or stirring for another 10-15 minutes at room temperature. If high background is experienced, 1% milk in PBS could be applied for both blocking and antibody dilution. 4. Wash plate 3 times with PBS-T. 5. (a) Incubate with biotinylated, affinity-purified rabbit IgG (0.1-0.5 μg/ml in PBS, 100 μl/well) at room temperature for 1 hour, followed by washing 6 times with PBS-T, then go to 8a. (b) Alternatively, incubate with affinity purified rabbit IgG (0.2-1 μg/ml in PBS, 100 μl/well) at room temperature for 1 hour, followed by washing 6 times with PBS-T, then go to 8b. 6. (a) Incubate with HRP-Streptavidin (1:4000-10,000 dilutions) in 0.2 % milk-PBS, 100 μl/well, at room temperature for 1 hour. (b) Incubate with HRP-anti-rabbit IgG (1:3,000-10,000 dilutions of 1 mg/ml or 0.25 μg/ml) in PBS, 100 μl/well, at room temperature for 1 hour. 7. Wash plate 8 times with PBS-T. 8. Develop color using TMB as a substrate (100 μl/well) and incubate at room temperature for 15-30 minutes without shaking. 9. Stop reaction by addition of 2N H2S04 (100 μl/well). Record the absorbance at 450 nm on a plate reader within 30 minutes of stopping the reaction. |
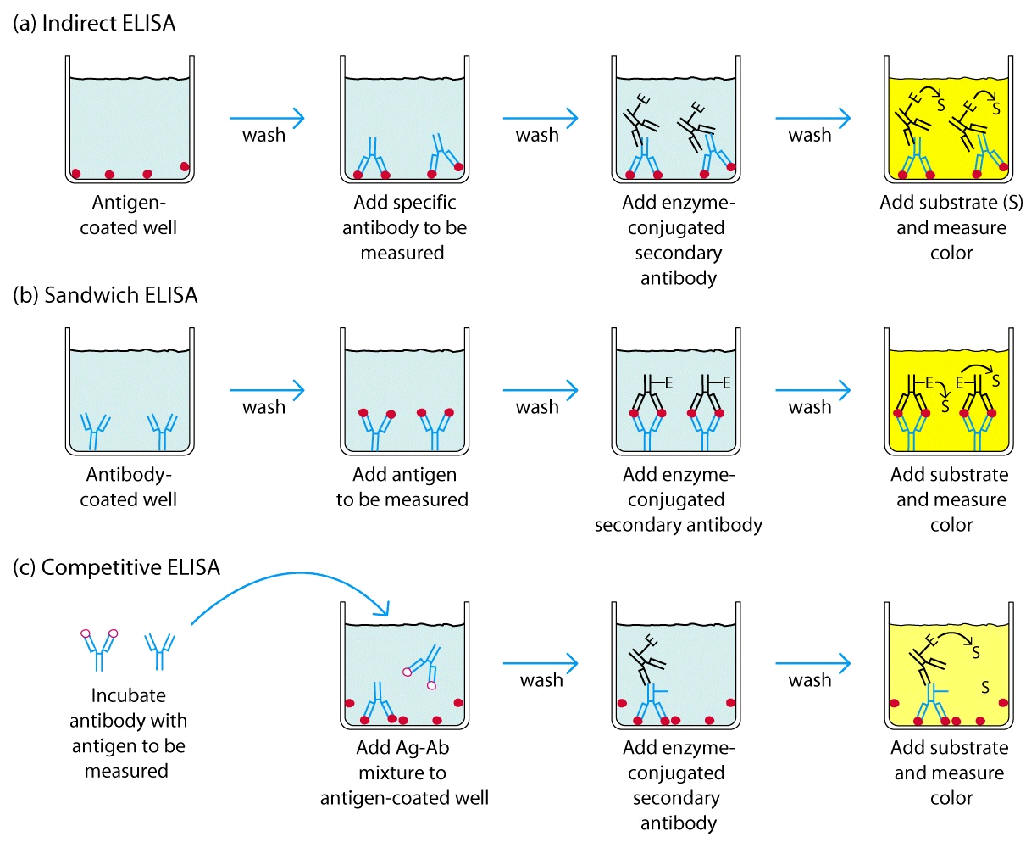
Sandwich ELISA Protocol
| 1. Before the assay, both antibody preparations should be purified and one must be labeled. 2. For most applications, a polyvinylchloride (PVC) microtiter plate is best; however, consult manufacturer guidelines to determine the most appropriate type of plate for protein binding. 3. Bind the unlabeled antibody to the bottom of each well by adding approximately 50 μL of antibody solution to each well (20 μg/ml in PBS). PVC will bind approximately 100 ng/well (300 ng/cm2). The amount of antibody used will depend on the individual assay, but if maximal binding is required, use at least 1 μg/well. This is well above the capacity of the well, but the binding will occur more rapidly, and the binding solution can be saved and used again. 4. Incubate the plate overnight at 4°C to allow complete binding. 5. Wash the wells twice with PBS. A 500 ml squirt bottle is convenient. The antibody solution washes can be removed by flicking the plate over a suitable container. 6. The remaining sites for protein binding on the microtiter plate must be saturated by incubating with blocking buffer. Fill the wells to the top with 3% BSA/PBS with 0.02% sodium azide. Incubate for 2 h to overnight in a humid atmosphere at room temperature. Note: Sodium azide is an inhibitor or horseradish peroxidase. Do not include sodium azide in buffers or wash solutions if an HRP-labeled antibody will be used for detection. 7. Wash wells twice with PBS. 8. Add 50 μL of the antigen solution to the wells (the antigen solution should be titrated). All dilutions should be done in the blocking buffer (3% BSA/PBS). Incubate for at least 2 h at room temperature in a humid atmosphere. 9. Wash the plate four times with PBS. 10.Add the labeled second antibody. The amount to be added can be determined in preliminary experiments. For accurate quantitation, the second antibody should be used in excess. All dilutions should be done in the blocking buffer. 11.Incubate for 2 h or more at room temperature in a humid atmosphere. 12.Wash with several changes of PBS. 13.Add substrate as indicated by manufacturer. After suggested incubation time has elapsed, optical densities at target wavelengths can be measured on an ELISA plate reader. Note: Some enzyme substrates are considered hazardous, due to potential carcinogenicity. Handle with care and refer to Material Safety Data Sheets for proper handling precautions. |
Competitive ELISA Protocol
| 1. For most applications, a polyvinylchloride (PVC) microtiter plate is best; however, consult manufacturer guidelines to determine the most appropriate type of plate for protein binding. 2. Add 50 μL of diluted primary antibody (capture) to each well. The appropriate dilution should be determined using an checkerboard titration prior to testing samples. PVC will bind approximately 100 ng/well (300 ng/cm2). The amount of antibody used will depend on the individual assay, but if maximal binding is required, use at least 1 μg/well. this is well above the capacity of the well, but the binding will occur more rapidly, and the binding solution can be saved and used again. Allow to incubate for 4 hrs. at room temperature or 4°C overnight. Note: If a purified capture antibody is not available, the plate should first be coated with a purified secondary antibody directed against the host of the capture antibody according to the following procedure: a. Bind the unlabeled secondary antibody to the bottom of each well by adding approximately 50 μL of antibody solution to each well (20 μg/mL in PBS). b. Incubate the plate overnight at 4°C to allow complete binding. c. Add primary capture antibody (as above). 3. Wash the wells twice with PBS. A 500 mL squirt bottle is convenient. The antibody solution washes can be removed by flicking the plate over a suitable container. 4. The remaining sites for protein binding on the microtiter plate must be saturated by incubating with blocking buffer. Fill the wells to the top with 3% BSA/PBS with 0.02% sodium azide. Incubate for 2 hrs. to overnight in a humid atmosphere at room temperature 5. Wash wells twice with PBS. 6. Add 50 μL of the standards or sample solution to the wells. All dilutions should be done in the blocking buffer (3% BSA/PBS with 0.05% Tween-20) Note: Sodium azide is an inhibitor or horseradish peroxidase. Do not include sodium azide in buffers or wash solutions, if an HRP-labeled conjugate will be used for detection. 7. Add 50 μL of the antigen-conjugate solution to the wells (the antigen solution should be titrated). All dilutions should be done in the blocking buffer (3% BSA/PBS with 0.05% Tween-20). Incubate for at least 2 hrs. at room temperature in a humid atmosphere. 8. Wash the plate four times with PBS. 9. Add substrate as indicated by manufacturer. After suggested incubation time has elapsed, optical densities at target wavelengths can be measured on an ELISA reader. Note: Competitive ELISAs yield an inverse curve, where higher values of antigen in the samples or standards yield a lower amount of color change. |
Sumber asli dapat dilihat di situs berikut : http://www.elisa-antibody.com
